Teachers Are Dropping Out
Is the US headed for an education crisis?

The growth rate of primary and secondary school teachers in the US has been in decline since 2018, with rates close to zero after the pandemic. Increases in attrition, rather than decreases in hiring, explain the declining growth.
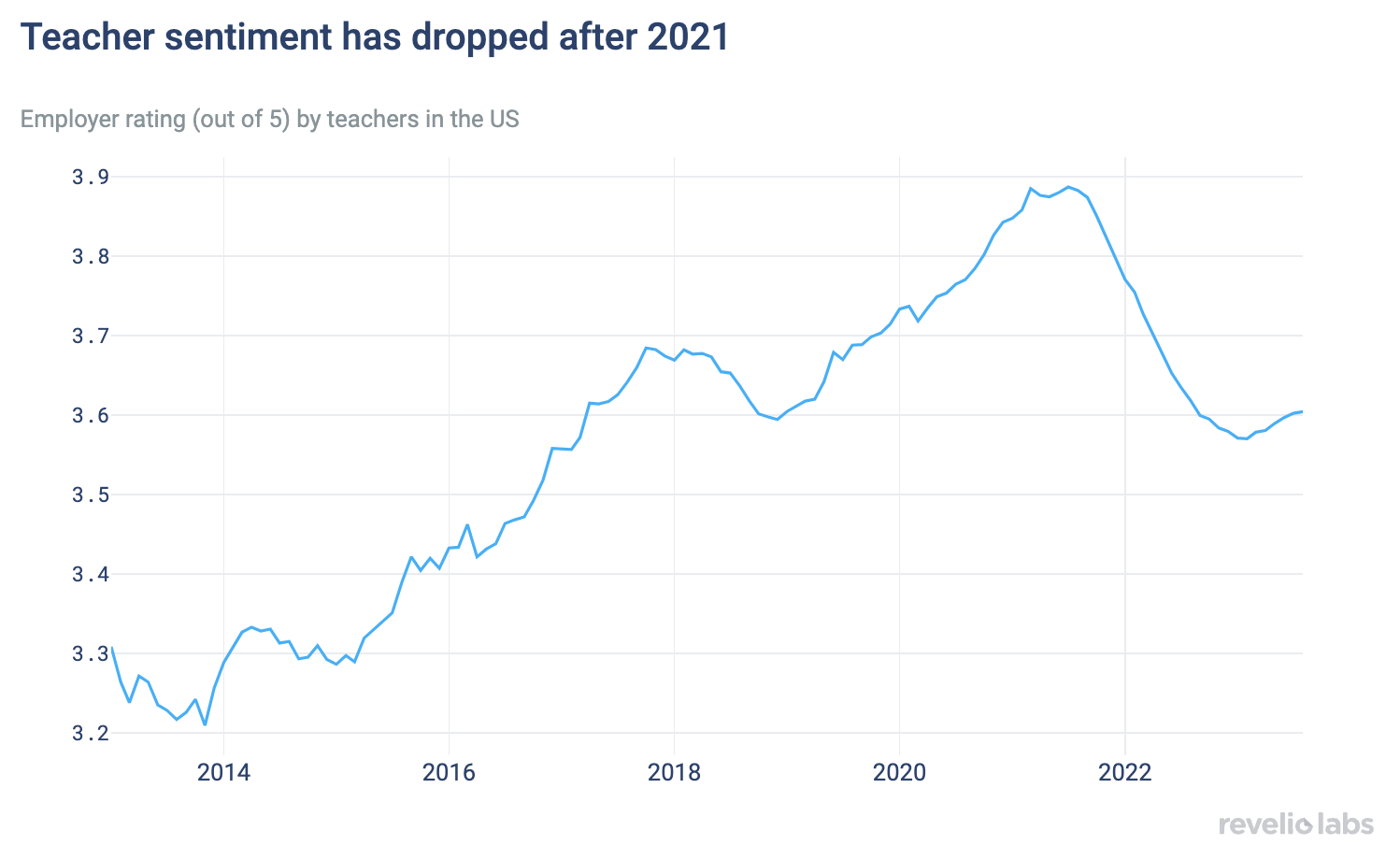
Teacher sentiment has also fallen post-pandemic, with teachers expressing displeasure with their lack of work-life balance, insufficient support from administrators, and low pay.
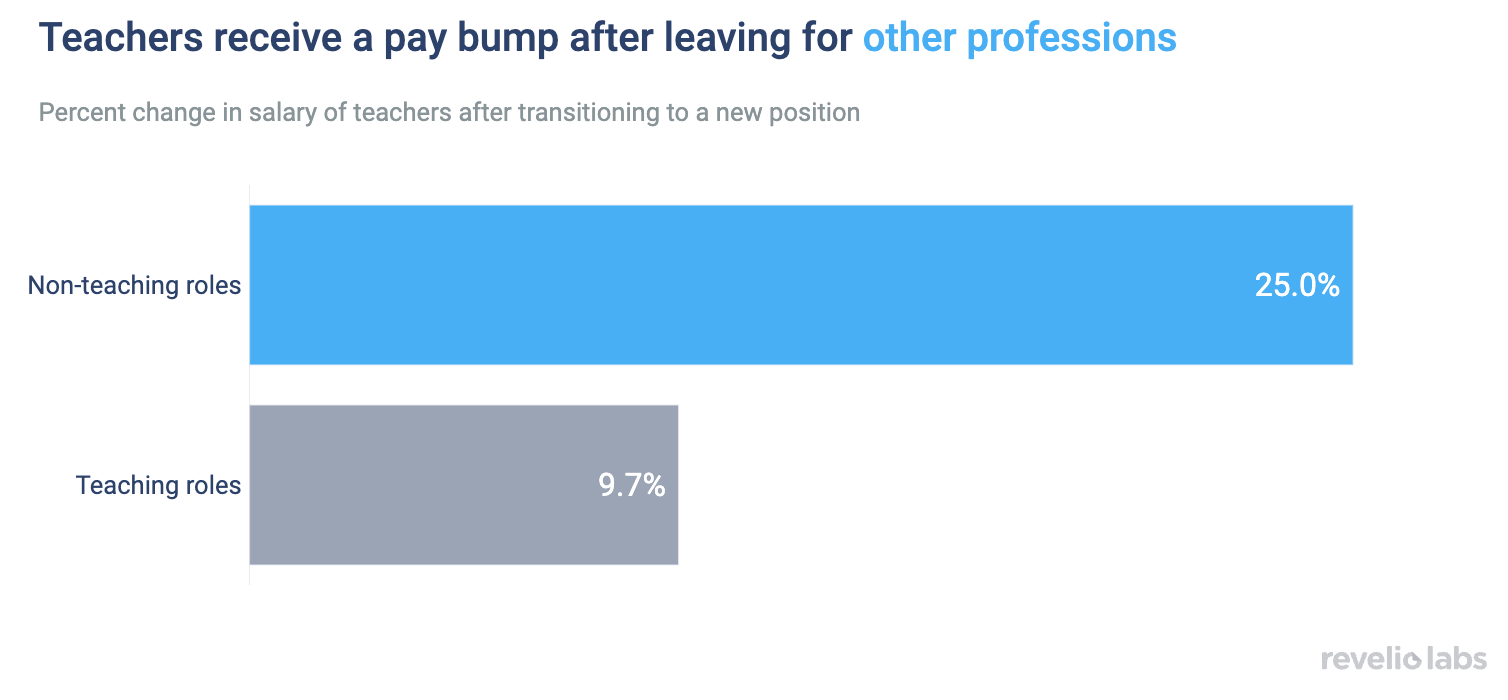
Teachers who leave their positions for a non-teaching occupation receive a 25% salary increase in their next role, relative to a salary increase of 9% for teachers who change jobs but remain in the profession
The teaching profession has been facing shortages and increased workforce attrition for several years, especially after Covid disrupted the education sector with online teaching and the consequent return to classrooms. Teacher attrition not only results in higher costs and inefficiencies for school districts but may also have detrimental effects on student achievement. In this newsletter, we examine these issues faced by the teaching profession in more detail.
Revelio Labs’ talent insights show that the growth rate of teachers in the US has been steady at 2% until 2018, when it started falling, dropping to nearly 0% during Covid. While the growth rate has rebounded slightly in 2022, it remains well below its pre-pandemic level.

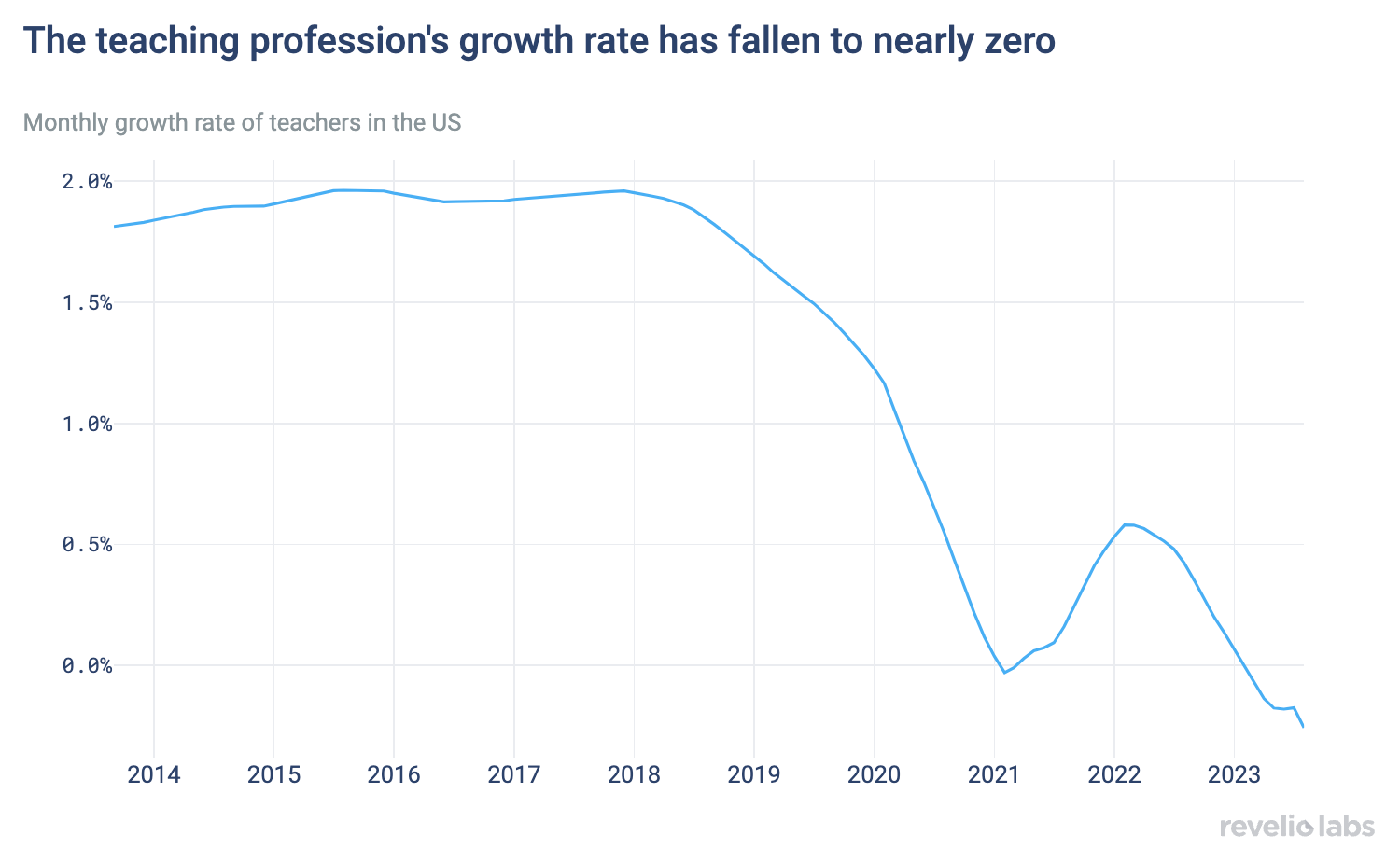
While both decreases in hiring and increases in attrition have contributed to this decrease in the growth rate, we find that attrition played a larger role: Teachers leaving their jobs accounted for two-thirds of the decline in growth. The attrition rate of teachers has increased by around 16% since 2018.
Sign up for our newsletter
Our weekly data driven newsletter provides in-depth analysis of workforce trends and news, delivered straight to your inbox!
What explains the increased workforce attrition of teachers? Examining ratings left by teachers about their employers, we find a sharp decline in sentiment, which has dropped by around 10% since its high in 2021.

Examining how topics mentioned in teachers’ reviews have changed after the pandemic sheds additional light on what is making them unhappy. Relative to 2019, the most commonly mentioned topics in negative reviews in 2022 include low pay and lack of support from the administration. These grievances may not be surprising: Teachers’ salaries have indeed not kept up with average salary growth in the US, as seen both in our data and in a report by the National Education Association.

Finally, where do teachers go after they leave their jobs? Revelio Labs talent insights show that of teachers who leave their positions, 58% continue in a different teaching position, 35% switch to a non-teaching position, and 7% do not report another position.
Those who transition from teaching to non-teaching roles receive a 25% pay increase in their next position. Teachers who transition to a different teaching position, including administrative roles, receive only a 9.7% pay increase. If teachers’ outside options prove to be more lucrative, schools may need to devote more resources to attracting and retaining high-quality teachers.